What Is a Competency Management System (CMS)?
A Competency Management System (CMS) is a structured framework designed to identify, assess, develop, and track the skills, knowledge, and behaviors essential for successful job performance within an organization. It goes beyond basic job descriptions by aligning employee competencies with strategic business goals.
In today’s fast-evolving talent landscape, a CMS is critical for strategic workforce planning, training needs analysis, succession planning, and performance management. By providing data-driven insights into employee capabilities and development gaps, it enables HR leaders to make informed decisions, build future-ready teams, and drive long-term organizational success.
A CMS provides a structured way to manage and measure workforce competencies, allowing HR teams and management to clearly define role requirements and track employee proficiency. It ensures ongoing skills development and workforce alignment with business objectives.
Core Elements of a Competency-Based Management Framework
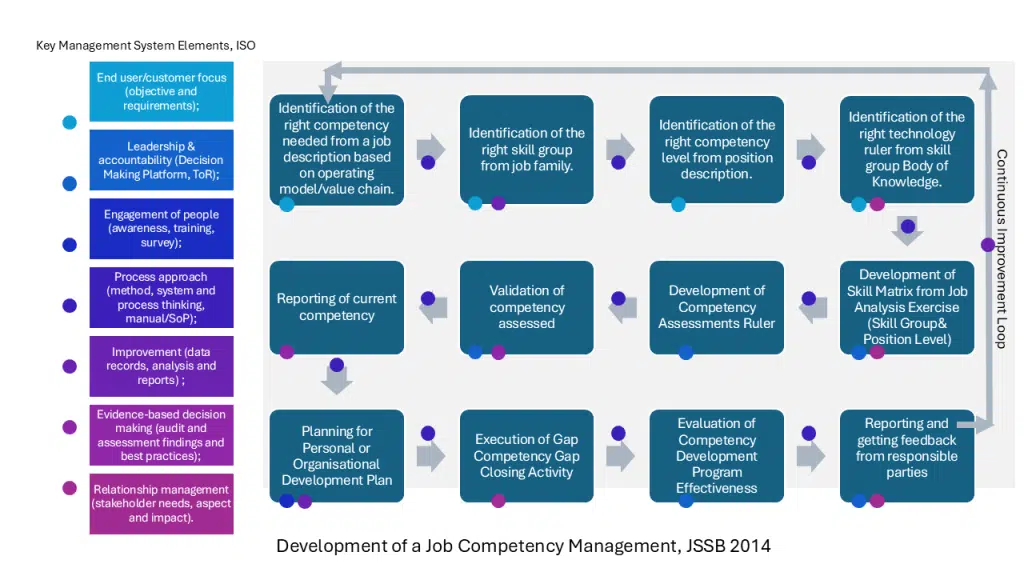
A management system is generally depicted to be having these several key elements ;
-
End user/customer focus (objective and requirements);
-
Leadership & accountability (Decision Making Platform, ToR);
-
Engagement of people (awareness, training, survey);
-
Process approach (method, system and process thinking, manual/SoP);
-
Improvement (data records , analysis and reports) ;
-
Evidence-based decision making (audit and assessment findings and best practices);
-
Relationship management (stakeholder needs, aspect and impact).
In developing a good Competency Management System, the above is translated and mapped into several key processes:
-
Identification of the right competency needed from a job description.
-
Identification of the right skill group from job family.
-
Identification of the right competency level from position description.
-
Identification of the right technology ruler from skill group Body of Knowledge.
-
Development of Skill Matrix from Job Analysis Exercise (Skill Group& Position Level)
-
Development of Competency Assessments Ruler
-
Validation of competency assessed
-
Reporting of current competency
-
Planning for Personal or Organisational Development Plan
-
Execution of Gap Competency Gap Closing Activity
-
Evaluation of Competency Development Program Effectiveness
-
Reporting and getting feedback from responsible parties
Usually, in a structured organisation good governance practice, there are several platforms and committees that take Competency as part of their Approvals Platform and Management Reviews, these are some of the example:
-
Human Resource Planning Committee (HRPC)
-
Human Resource Talent Effectiveness Committee (HRTEC)
-
Human Resource Compensation,
-
Benefit, and Discipline Committee (HRBDC)
-
Talent Capital Committee (TCP)
and others with relevant Terms of Reference.
Step-by-Step Methodology to Build a Competency Management System
-
Foundation Phase – Job Analysis and Role Mapping
At this phase, job analysis is carried out to understand the requirements of each role. From this, related roles are grouped into skill clusters, and a competency model is developed. This model defines the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for each position and provides a standardized framework for managing competencies across the organization.
-
Assessment Phase – Validating Competencies
This phase is where appropriate tools and instruments are developed to evaluate competencies. These tools are validated to ensure accuracy and reliability before being used in actual assessments. The assessment process may include self-assessments, manager evaluations, 360-degree feedback, or structured assessment centers, depending on the complexity of the roles and organizational requirements.
-
Gap Analysis Phase – Identifying Skill Gaps
In this gap analysis phase, the results of the assessments are compared against the desired competency levels. This analysis identifies specific skill gaps at both the individual and organizational levels. Based on these findings, targeted development plans are created to close the gaps and prepare employees for current and future demands.
-
Execution Phase – Development and Training Plans
Once development plans are in place, the execution phase begins. This involves implementing structured training programs, coaching, mentoring, and other developmental interventions aimed at enhancing employee capabilities. These activities are closely aligned with organizational priorities to ensure they deliver measurable results.
-
Evaluation Phase – Measuring Outcomes
After execution, the evaluation phase takes place to measure the effectiveness of the development activities. Competency assessments are revisited to track improvements, and data is used to drive a continuous improvement loop, ensuring that the competency management system evolves in response to changing business needs.
-
Governance Phase – Oversight and Review
Finally, the governance phase ensures oversight and accountability. Regular audits, detailed reporting, and structured feedback mechanisms are put in place to keep leadership informed and engaged. This governance framework supports informed decision-making and promotes the long-term sustainability of the competency management system.
Best Practices for Sustaining a Competency Management System
Implementing best practices is crucial to ensure the effectiveness and sustainability of a Competency Management System.
-
Align with HRIS or LMS Platforms
One of the key practices is to align the competency system with HRIS or LMS platforms. This integration enables automation of processes such as tracking assessments, managing learning interventions, and maintaining competency records, thereby improving efficiency and reducing administrative workload.
-
Use Multi-Method Competency Assessments
Another important practice is the use of multi-method assessments, such as 360-degree feedback, psychometric tests, and assessment centers. By applying different assessment methods, organizations can gather a more holistic view of an individual’s competencies, reducing bias and increasing the validity of results.
-
Integrate with Performance & Succession Planning
It is also essential to integrate the competency framework with succession planning and performance management. This alignment ensures that competency data not only supports individual development but also strengthens talent pipelines, supports career progression, and links directly to organizational performance objectives.
-
Establish Competency Governance Councils
In addition, organizations should establish competency councils for governance and periodic review. These councils, typically comprising HR leaders, department heads, and subject matter experts, play a critical role in ensuring that competency frameworks remain relevant, consistent, and aligned with evolving business strategies.
-
Leverage Real-Time Analytics and Dashboards
Finally, leveraging analytics and dashboards for tracking and reporting enhances decision-making. By using real-time data and visual insights, leaders can identify trends, monitor progress, and make evidence-based decisions on workforce development initiatives. This data-driven approach supports continuous improvement and ensures that the competency management system delivers measurable value.